The Secret That All The Medical Laboratory Design Layout Experts Don't Want You To Know
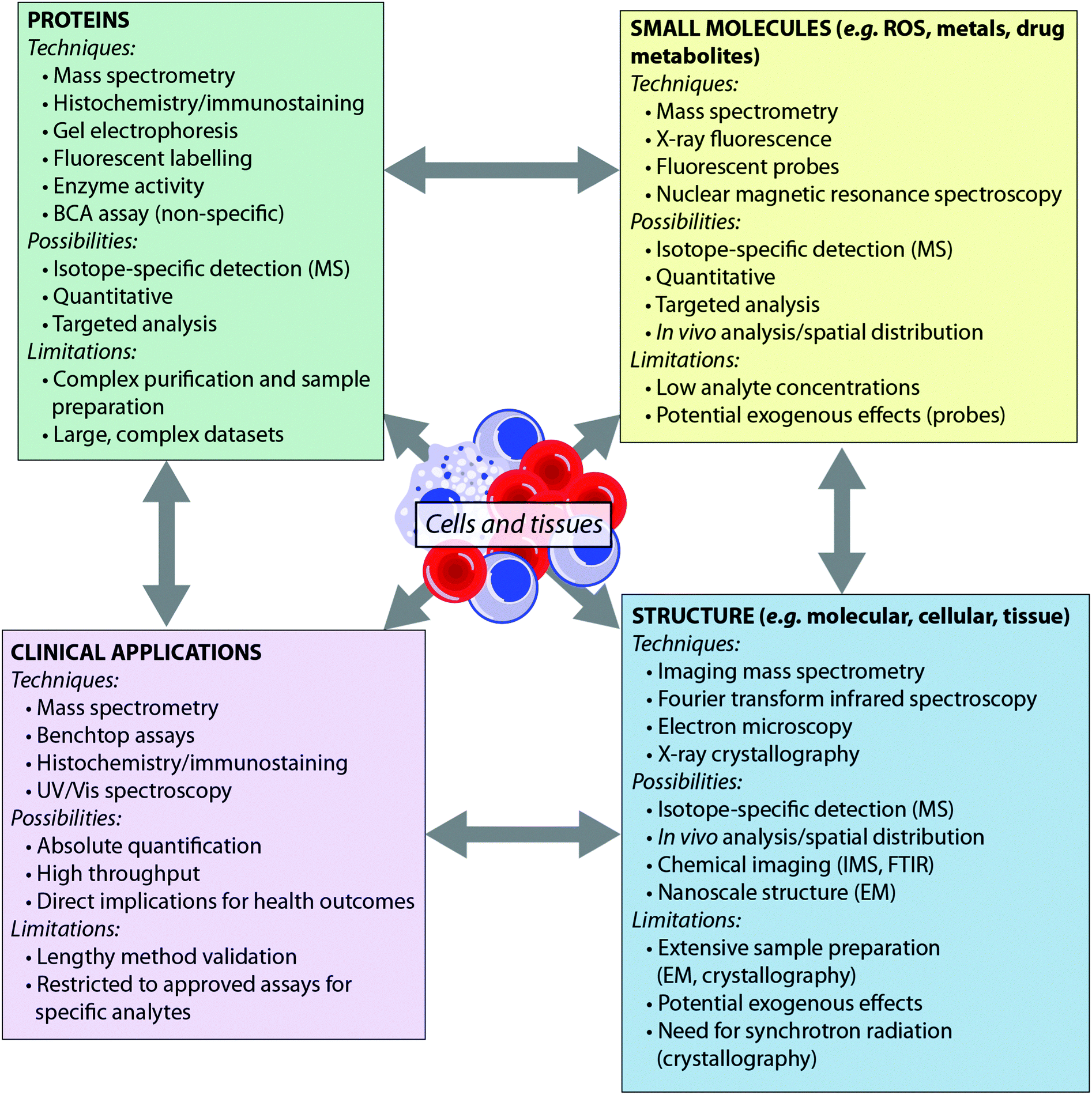
In order to avoid the high background disturbance signal in the low-mass region (
Considering that the introduction of chemistry, private investigators have actually required to know the identity and quantity of the products with which they are working. Basic instruments (such as photometers and electrogravimetric analysis device )were readily available at the end of the 19th century, crucial analysis did not flourish till well into the 20th century. Some analytical chemists differentiate in between an analysis, which involves all the actions, and an assay, which is the lab part of the analysis.
Throughout this preliminary step of analysis, a portion of a bulk product is removed in order to be assayed. The portion should be picked so that it is representative of the bulk material. When selecting a sampling program, it is essential that the expert has an in-depth description of theinformation required from the analysis, an estimate of the precision to be accomplished, and a price quote of the quantity of time and cash that can be invested on tasting. It is beneficial to talk about with the users of the analytical results the type of data that is wanted. Typically the accuracy of an analysis is increased by acquiring numerous samples at differing areas( and times )within the bulk material. As an example, analysis of a lake for a chemical toxin will likely yield incorrect results if the lake is tested just in the centre and at the surface area. The homogeneity of the bulk material influences the number of samples required. If the product is homogeneous, just a single sample is needed. More samples are needed to get a precise analytical outcome when the bulk material is heterogeneous. The disadvantages of taking a bigger variety of samples are the included time and expense. Analytical chemists utilize their understanding of chemistry, instrumentation, computers, and stats to fix issues in practically all areas of chemistry. Analytical chemistry is the science of obtaining, processing, and interacting details about the composition and structure of matter. In other words, it is the art and science of determining what matter is and just how much of it exists. They utilize their knowledge of chemistry, instrumentation, computers, and data to fix issues in almost all locations of chemistry. Their measurements are utilized to assure compliance with environmental and other policies; to ensure the safety and quality of food, pharmaceuticals, and water; to support the legal process; to help doctors diagnose disease; and to supply chemical measurements necessary to trade and commerce. They do fundamental laboratory research, establish procedures and products, style instruments used in analytical analysis, teach, and work in marketing and law. Analytical chemistry is a challenging profession that makes significant contributions to lots of fields of science. Analytical chemists are generally included with making measurements utilizing sophisticated advanced computer-controlled instrumentation in government labs as well as in labs in the chemical, pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and food markets. Analytical chemists are likewise suited for positions as quality control professionals to make sure that treatments and protocols are followed. A strong background in chemistry and good lab, computer system, and communication skills are necessary for dealing with a variety of chemical measurements. Due to the fact that analytical chemistry is a service discipline, integrating the skills of a chemical expert with knowledge of the distinct problems of other chemical disciplines( such as natural, polymer, inorganic, and ecological chemistries) is an important property. analytical chemistry testing. Info recovered from American Chemical Society: Analytical Chemistry and Payscale: Typical Analytical Chemist Wage. Analytical methods have actually been extremely important considering that the early days of chemistry, set up to determine which elements existed in a sample. This period saw the development
of organized essential analysis, consisting of making use of basic spectrometric techniques that have actually been continuously improved throughout the 20th century . Separation sciences likewise emerged really quickly from the start of contemporary chemistry, until they experienced a significant boom with the arrival of complex instruments. This holds true for qualitative analyses, such as: chemical tests, such as the Kastle-Meyer test for the detection of blood; and flame tests, to find the existence of certain metal ions or other elements. Analytical approaches have been enhanced significantly through the development of technological instruments. Advances in mass spectrometry Mass spectrometry (MS)used to proteomics has literally blown up considering that the 2000s - analytical chem lab. The most mature criteria are sensitivity, resolution, and sample reading speed. Today, a high-throughput approach is made possible, making the analysis of complex samples more inexpensive. Hybrid triple quadrupole (TQ )MS has made significant progress in quantitative MS, which nevertheless has technical limitations. The application of MS to the research study of complexes such as antibody/antigen complexes is made possible by a method called hybrid LBA/LC-MS or immunoassay spectrometry. Innovation Couplings While among the most effective innovation couplings, chromatography combined with mass spectrometry, as explained above, other couplings increase the abilities of the technologies significantly. This holds true in specific with capillary electrophoresis, which, when it is preparatory, can be coupled with MALDI-To, F analysis for the recognition of separated species. When coupled with mass spectrometry,
Are You Getting The Most Out Of Your Analytical Chem Lab?
CE dramatically increases its analytical capabilities, particularly in the characterization of clusters obtained during bioproduction. The rise of metabolomics Metabolomics is the large-scale research study of little particles, typically called metabolites, within cells, biofluids, tissues or organisms. Collectively, these little particles and their interactions within a biological system are called

the metabolome. Mass spectrometry( MS )and nuclear magnetic resonance(NMR)have actually ended up being the most common techniques in metabolomics research studies, and each has its own advantages and restrictions. NMR spectroscopy is quantitative and does not require additional sample preparation actions such as separation or derivatization. NMR spectroscopy has limitations in regards to level of sensitivity. Analytical chemistry at the service of biological research study Regular analysis Many analysis procedures exist, and the required reagents and instruments are well defined and noted. These standard methods can be licensed for certain usages by companies such as AOAC International or ISO. Analysis requiring more advancement Procedures that have never been applied in unique cases, such as the analysis of new biomarkers or the modification of standard conditions, may require technique development. To be in line with the requirements of Great Production Practice (GMP), the approach should be verified according to a documented procedure. Analytical chemistry plays a massive function in our society, such as in drug manufacturing, process control in market, environmental tracking, medical diagnostics, food production, and forensic studies. It is also of fantastic value in different research study areas. laboratory set up. Analytical chemistry is a science that is directed towards creating new understanding so that chemical analysis can be improved to react to increasing or brand-new demandscall it a"approaches science" if you desire. In time, analytical chemistry has altered.
Early on, the focus was very much on elemental analysis and speciation; for example the work of Torbern Bergman(specified to be the very first"analytical chemist "worldwide)in Uppsala in the late seventeenth century [1] Analytical technologies and instruments were for hundreds of years established in-house or in department tool shops. The possibly just exception to this is the ongoing process of miniaturisation and combination of analytical platforms into intricate systems. The research study area of analytical chemistry has been migrating from earlier instrument building and method development to the primary focus being on approach advancement and applications of analytical chemistry. Method development in itself involves acquiring quicker, more delicate, simpler, more complex/informative and/or more environmentally sustainable analytical methods. Mass spectrometry is now an analytical tool for chemists, pharmacologists, medical specialists and biologists however in the past was in the hands of pure ion physics. The significant biological needs have actually driven the development with rocket speed. Activities in sustainable advancement as in chemical market, where eco-friendly resources are used more effectively, likewise need higher efforts of analytical chemistry and chemistry at large. Analytical chemistry will continue to be an important part of undergraduate education in chemistry, not only for natural researchers and engineers but also for real translational and cross-disciplinary initiatives involving biologists and medical students and even within social science(e. g. what is analytical chemistry. financial experts within a circular economy and bioeconomy )and law(e. within environmental legislation and sustainable advancement, copyright protection). There is also a need for informed analytical chemists in the future. Analytical chemistry is necessary as evidenced by a current survey by the European Association for Chemical and Molecular Sciences(Eu, Che, MS)that got responses from 4500 chemists and chemical engineers in Europe, of which 15 %were analytical chemists. There is an apparent need to continue to take care of research study and education in analytical chemistry, and to follow existing patterns and ramifications within the topic, as well as in cross-disciplinary efforts where analytical chemistry plays a significant function. One forum for discussing research study and education in analytical chemistry is the Euroanalysis conference. Euroanalysis is held every 2nd year, and the conference covers all elements where analytical chemistry plays a function, including fundamental and applied sciences. More than 500 abstracts were sent, of which 145 were given as oral presentations and 273 were provided as poster discussions. In addition, 28 of the posters were pitched in special poster pitch sessions. There were 10 plenary lectures and 32 keynote lectures. Three major awards were handed out throughout Euroanalysis XIX. The Robert Kellner Award was offered to Luigi Mondello, University of Messina, Italy, who gave a lecture entitled" Different approaches to multidimensionality in chromatographic separations paired to mass spectrometry detection to deal with tough analytical tasks ". Lastly, the Heinrich Emanuel Merck Award for Analytical Chemistry was offered to Francesco Ricci, and he lectured entitled"Nature-inspired DNA-based nanodevices for picking up applications". Overall, the conference had 509 individuals from 53 various nations. The leading 10 countries were Sweden( 138 ), Germany(43), Spain (27), the Czech Republic (26 ), Russia (24), Italy(22 ), Japan(16 ), the UK(15 ), the Netherlands( 12)and Belgium (12). Of note was the excellent(and extremely pedagogic )lecture given by the Nobel laureate Stefan Hell about microscopy with a resolution of the size of a molecule, demonstrated by doughnuts and devils [3] Another interesting lecture was provided by Lutgarde Buydens, talking about person science; that is the use of non-scientists(residents )to gather evidence-based data, for instance, for analytical health monitoring [4] The conference also consisted of a session about education in analytical chemistry, which had contributions about a new Erasmus Mundus programme, lab abilities among chemical engineering trainees, formalisation of validation standards, how to present metrology concepts to students, problem-based learning in analytical chemistry and industry-supported education programmes, among others. A few of the discussions at Euroanalysis XIX are represented in this topical collection of short articles. Food and forest research study contributions include, for circumstances, high-value phenols and carbohydrates in wood pyrolysis liquids and the phenolic profile and antioxidant activity of honey. The greatest impression from the Euroanalysis conference programme and the Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry topical collection of short articles is the breadth of analytical.
chemistryfrom fundamentals to applicationsdemonstrating the effect of analytical chemistry in society specifically relating to ecological and health elements. SHALL WE PLAY A"SHALL "VS." SHOULD"CHALLENGE? Should you take this quiz on "shall"versus "should"? It needs to show to be a fast difficulty! Question 1 of 6Which form is utilized to state an obligation or duty someone has? We may, nevertheless, notice Heinrich Rose i and Friedrich WShler, 2 who, having developed the outcomes of their teacher Berzelius, and integrated them with their own valuable observations, applied terrific impact on the development of analytical chemistry by releasing works which contained admirable accounts of the then known methods of analysis. Analytical chemists can specialise in locations as differed as toxicology, pharmaceuticals and forensics. Common employers Certifications and training Secret skills Analytical chemists analyse samples using a series of techniques such as electro-chromatography, high efficiency liquid chromatography and spectroscopy. They are utilized by a variety of public and personal sector organisations, and can specialise in areas such as toxicology, pharmaceuticals, quality control or forensics. Vacancies generally bring in strong competitors, specifically those for graduate training schemes with significant business. For this factor, applications(especially those to bigger companies)need to be made early in the scholastic year. Opportunities are promoted online, by careers services, in nationwide newspapers, in appropriate clinical publications such as New Scientist, Nature, Chemistry World and their online equivalents, and in other journals published by clinical professional organizations. The recruitment procedure is likely to involve a technical interview. Read our post on technical interviews to discover what these include and how you can tackle them. If you wish to discover out what your salary might appear like, take a look at our post on how much you might make in science on our TARGETcareers website. 1 or above )in an appropriate subject such as chemistry, applied/analytical chemistry or biochemistry. There are also chances for geochemists, products scientists, mathematicians and environmental scientists within the field of analytical chemistry. Practical research/laboratory work experience is valuable, although complete training on the job is often readily available. A postgraduate credentials in analytical chemistry might be useful for careers in research study or for profession improvement in the long term and might enable entry to the occupation at a more senior level. Membership of the Royal Society of Chemistry( RSC)might assist you advance to advanced positions. This is a recognition of achievement acquired through expert activity, and might be awarded three years after graduation. Members might consequently be awarded the status of fellow( FRSC )or chartered chemist (CChem), representing professionalism, achievement and a high level of specialised subject understanding. Employers progressively search for both research study and transferable abilities consisting of: a logical and independent mind the inspiration and capability to solve complicated issues a systematic technique to jobs theoretical understanding of analytical strategies the capability to establish and verify brand-new techniques outstanding IT skills mathematical and analytical capability teamworking responsibility communication and discussion skills. You'll require a strong science-based degree together with good technical abilities and an eye for information to end up being an analytical chemist, As an analytical chemist, you'll utilize a variety of techniques to examine the chemical composition of substances. Your aim is to recognize and comprehend the compound and how it behaves in various conditions. In the pharmaceutical market, for example, you would be included throughout the drug advancement process. This would include studying the physical or chemical residential or commercial properties of drug compounds and solutions, with a view to figuring out the quality and stability of drug products. As an analytical chemist your jobs can differ, however you'll generally need to: prepare and analyse samples from numerous sources to supply info on compounds or amounts of substances presentuse analytical strategies and instrumentation, such as gas chromatography(GC ), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), ion chromatography, electrochromatography, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry(LC-MS )and spectroscopy(infrared and ultraviolet, amongst others ), to investigate chemical compositionsinterpret information and fulfill stringent standardson documents when taping datareview and examine experiments and analysespresent clinical outcomes to relevant groups compose reports and research papersdevelop new strategies for the analysis of drug products and chemicalswork collaboratively with cross-functional teamsliaise with customers, personnel and suppliers, along with stakeholders and partnersbe mindful of, and keep up to date with, health and safety issueskeep as much as date with the newest clinical and technical trendsvalidate techniques and equipment. Analytical chemists in the first couple of years of their career can make in the area of 22,000 to 34,000. As you again even more experience and take on more senior roles, wages can vary from around 30,000 to 45,000. Principal analytical chemists with substantial experience and lab managers might earn over 50,000. Beginning wages may be greater for Ph, D holders, but this isn't a requirement for the majority of analysis roles. There are more specialist functions, nevertheless, that can require a Ph, D.Benefits also vary according to the company, however may include free or subsidised medical insurance coverage. Earnings figures are planned as a guide just. Part-time work and profession breaks are in some cases possible. Self-employment is really not likely due to the significant monetary investment in equipment and staffing, plus the requirement for accreditation. There are chances for freelance consultancy work, although large companies tend to have their own professionals. You'll generally work in multidisciplinary teams and communicate with scientists and customers from both within and outside the business. Jobs are offered throughout the UK and tend to be concentrated in large towns and cities. Research and development (R&D)work can be more typically discovered in the south of England. You require to be comfy with working to tight deadlines and fixing problems as quickly as possible. Regular analysis can involve doing the same job for extended periods of time, although you're less likely to do this in more senior posts. If working for a big company, however, you may need to move between websites to help keep track of safety conditions (laboratory quality management system). Overseas travel is uncommon, although secondments abroad might be possible as you reach greater grades. You'll need a degree, typically a 2:1 or greater, in chemistry or a related subject such as applied/analytical chemistry or biochemistry to end up being an analytical chemist. Look for degree courses certified by the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC). Entry-level tasks, typically in analytical specialist roles, are readily available for those with an HND. These kinds of function are typically an entry requirement for a degree apprenticeship, which integrates paid deal with academic research study at degree level. Some big employers run graduate training plans. A pre-entry postgraduate certification isn't needed, although having an MSc or Ph, D in analytical chemistry or an associated topic could be helpful for your longer-term career or for tasks in research.Search postgraduate courses in analytical chemistry. You will require to reveal: self-esteem and motivation to investigate and fix intricate problemsthe capability to arrange, prioritise and set up work to meet demands set by the department, business or external customerexcellent composed, oral and presentation skills and the capability to communicate technical info to non-technical peoplea great standard of numeracy and skills in information analysisstrong technical problem-solving abilities, IT and innovation skills to deal with sophisticated techniquescreativity and the capability to utilize your initiative for independent workeffective collaborative and teamworking skillsa patient and systematic approach to workresearch skillsobservation abilities and attention to detailthe ability to perform jobs to quality requirements in a safe environment. Practical research or lab experience is helpful. This can be acquired from a year in industry, a summer work placement or an internship with bigger business. Look for positionings and internships at Chemistry World Jobs. There might be chances to deal with smaller business on summer projects. It's also possible to gain useful experience as a lab technician. Getting work experience helps you to establish your practical abilities and develop a network of contacts for potential tasks when you finish. Nevertheless, if you have little or no experience in this location you ought to still make an application for tasks. Full training is often available for entry-level tasks and companies will understand you've gotten essentialunderstanding from your degree. Work can be found in a range of clinical markets and typical companies consist of: academiaagrochemical companiesbiotechnology or agreement research organisationschemical and polymer manufacturersenergy companiesenvironmental agenciesfood and drink companiesforensic companiesgovernment agencieshospital laboratoriesmultidisciplinary consultancy or screening companiespetrochemical companiespharmaceutical companiespublic health laboratoriesresearch and advancement organisationswater business. Research study and development is performed in a variety of organisations in the business, education and public sector. Research is significantly collaborative throughout all clinical fields, with many partnerships between company and academia. Search for task vacancies at: A number of the significant companies advertise tasks and graduate training schemes by themselves sites, so inspect these frequently. Recruitment firms commonly deal with jobs for lab-based functions and require practical experience. Agencies you may want to examine include: A lot of training is on the task,provided by senior colleagues, and might be supported by brief courses. You'll generally receive recorded training treatments in the strategies you'll use. Providers of technical equipment or expert software application might also offer training. In addition, training may be provided through a programme of continuing professional advancement(CPD).